Introduction of cleaning method and temperature
Browse Volume:1197 Classify:Support
Method of cleaning
Ordinary cleaning methods generally cannot reach the hole, and the reaction products of the core material and other pollutants in the hole will produce repeated pollution in the subsequent process. Whether using organic solvent or cleaning solution, it is easy to introduce new pollution sources, but using ultrasonic cleaning technology can realize no repeated pollution, and can penetrate into the MCP hole effect. Ultrasonic wave with adjustable frequency and sound intensity should be used to test MCP of different materials and aperture to determine the actual process parameters.

Cavitation
For the cleaning of pore size 6-12 μmMCP, when the medium liquid is water and ethanol, the ultrasonic wave with cavitation threshold of about 1/3 W/cm2, sound intensity of 10-20 W/cm2 and frequency of 20-120 kHz can be used for cleaning. Table 1 shows the apparent and electrical performance test results of MCP with different plate sizes in the same section after ultrasonic cleaning at different frequencies. It can be seen from the test results that the ultrasonic wave with a frequency of more than 40 kHz should be used to clean the small particle pollutants below 1μm.Suggest you have a look granboultrasonic cleaner. It can be applied to Blind cleaning.
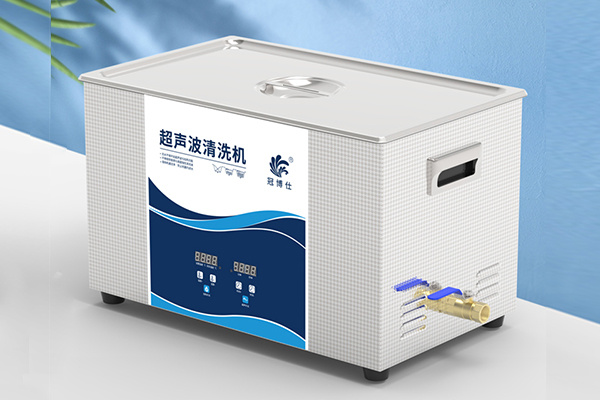

ultrasonic cleaner
Cleaning temperature
In the process of silicon wafer cleaning, the temperature of cleaning solution is a key factor. Suitable cleaning temperature can speed up the removal of oil pollution, get the best cleaning effect. When the silicon wafer is immersed in the cleaning solution, the oil on the silicon wafer will expand, and the force within the oil and between the oil and the silicon wafer will weaken. The higher the temperature, the greater the oil expansion, the weaker the force will be, and the easier the surfactant molecules will pry the oil from the surface of the silicon wafer. At the same time, the change of temperature can lead to the change of micelle properties and the dissolution of the soluble substance in micelles. The polyoxyethylene chain (CH2CH2O) n of polyoxyethylene surfactant produces hydration in water and forms hydrogen bonds with the hydrogen in water molecules.
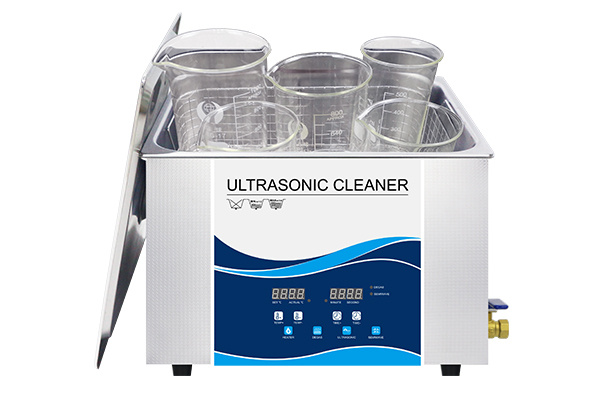
ultrasonic cleaner
With the increase of temperature, hydrogen bonds weaken and some even break, hydration decreases, micelles are easy to form, the aggregation number of micelles also increases significantly, and the solubility of oil and other pollutants increases. This situation is conducive to the cleaning of silicon wafers. When the temperature rises to about 60℃, polyoxylethylene chain (CH2CH2O) n accelerates dehydration and produces shrinkage, so that the micelle dissolution space decreases, the capacity decreases, and the cleaning solution changes from transparent to emulsion. This temperature is called the turbidity point temperature of the solution. Only when the temperature is close to the turbidity point of the surfactant solution, the solubilization ability is the strongest, so the temperature of the cleaning solution is set at 60℃.
 Granbo Ultrasonic
Granbo Ultrasonic














Hello!